
In the case of overactive bladder, your doctor may suggest a number of strategies, including bladder training, electrical stimulation, drug therapy, and, in severe cases where all other treatments have failed, surgery.īladder training. The treatment for a bladder control problem depends on the cause of the nerve damage and the type of voiding dysfunction that results. What are the treatments for overactive bladder? The doctor may also use an electromyograph (EMG), which uses wires with pads placed on the lower abdomen to test the nerves and muscles of the bladder. An electroencephalograph (EEG) is a test in which wires with pads are placed on the forehead to sense any dysfunction in the brain.

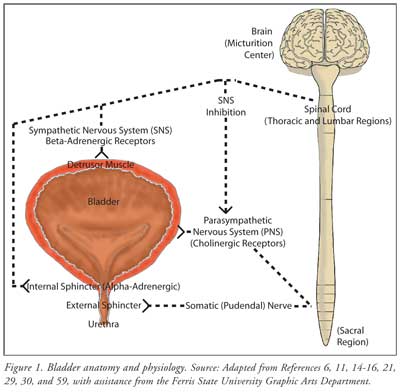
The doctor may use different types of equipment x rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computerized tomography (CT) scans to take pictures of the urinary tract and nervous system, including the brain.ĮEG and EMG. These tests involve measuring pressure in the bladder while it is being filled to see how much it can hold and then checking to see whether the bladder empties completely and efficiently. Three different kinds of tests might be used: If nerve damage is suspected, the doctor may need to test both the bladder itself and the nervous system, including the brain. Your doctor can use this information to narrow down the possible causes for your bladder problem. How will the doctor test for nerve damage and bladder control problems?Īny evaluation for a health problem begins with a medical history and a general physical examination. In addition, some children are born with nerve problems that can keep the bladder from releasing urine, leading to urinary infections or kidney damage. accidents that injure the brain or spinal cord.Many events or conditions can damage nerves and nerve pathways. Urine retention may also lead to overflow incontinence. Or urine that stays too long may lead to an infection in the kidneys or bladder. If the bladder becomes too full, urine may back up and the increasing pressure may damage the kidneys. For some people, nerve damage means their bladder muscles do not get the message that it is time to release urine or are too weak to completely empty the bladder. If the nerves to the sphincter muscles are damaged, the muscles may become loose and allow leakage or stay tight when you are trying to release urine. Sphincter muscles surround the urethra and keep it closed to hold urine in the bladder. urge incontinence leakage of urine that follows a sudden, strong urge to urinate.urinary urgency the sudden, strong need to urinate immediately.urinary frequency defined as urination eight or more times a day or two or more times at night.The symptoms of overactive bladder include Damaged nerves may send signals to the bladder at the wrong time, causing its muscles to squeeze without warning. Nerves that work poorly can lead to three different kinds of bladder control problems. What bladder control problems does nerve damage cause? A nerve problem might affect your bladder control if the nerves that are supposed to carry messages between the brain and the bladder do not work properly. They also carry messages from the brain to the bladder, telling muscles either to tighten or release. Nerves carry messages from the bladder to the brain to let it know when the bladder is full. Neurogenic Bladder Nerve Disease and Bladder Controlįor the urinary system to do its job, muscles and nerves must work together to hold urine in the bladder and then release it at the right time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
